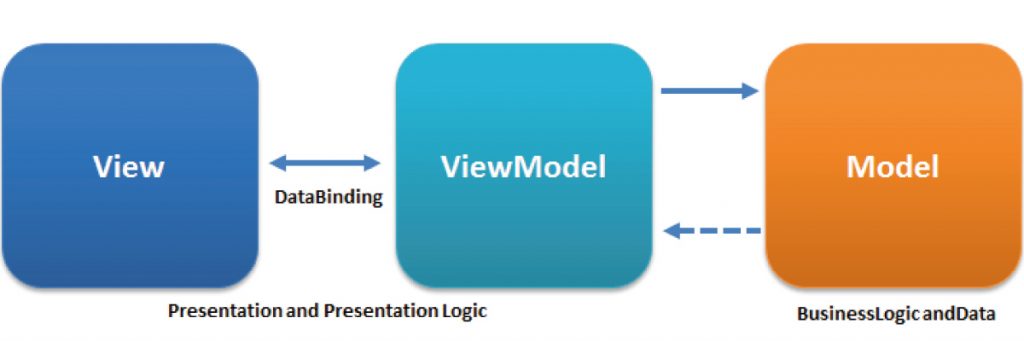
Using the MVVM architecture, it is possible to maintain a complete separation between the code responsible for the user interface (the View), the code responsible for the data itself (the Model), and the code responsible for the efficient connection between the View and the Model while providing an answer to problems related to the use of threads (the GUI is rendered using a thread that should be separated from the thread responsible for working with the data itself).
The Graphics User Interface Thread
Whether you develop a stand-alone desktop application with GUI in Java or in another programming language, most likely that you will be requested to make sure that all the interaction with the GUI, including its creation, will take place through the specific thread that is responsible for rendering the user interface. Usually, in most platforms, this is the case. In addition, the thread that renders the user interface cannot be blocked. It will freeze the user interface. As a result of that, the interaction with the data (Model) must be carried through another thread. These are the main limitations that contributed to the emergence of the MVVM architecture. MVVM stands for Model, View, and ViewModel, a third component that handles the connection between the View and the Model.
The MVVM Architecture Seminar
We have recently developed the MVVM Architecture professional seminar. You can arrange the delivery of this seminar in your company for your software developers. Through this seminar your developers will become highly trained in implementing this architecture.
Don’t mix up the MVVM with the MVC architecture. These are two different architectures. The implementation of MVVM can be carried out using nearly any programming language and any platform.










